Thursday, 22 September 2011
Q1. Zinc nitrate reacts with aqueous ammonia (NH4OH) to form a salt and a base. (i) Name the salt and the base. (ii) Describe the observations for the reaction. (iii) Write a chemical equation for the reaction (include state symbols). (iv) Write an ionic equation for the reaction.
Answers:
(i) The salt formed is ammonium nitrate and the base formed is zinc hydroxide.
(ii) When zinc nitrate reacts with aqueous ammonia, sodium nitrate and zinc hydroxide (white precipitate) is formed.
(iii) Zn(NO)3(aq) + 2NH4OH(aq)
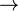 Zn(OH)2(s) + 2NH4NO3 (aq)
Zn(OH)2(s) + 2NH4NO3 (aq)(iv) Zn2+
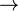 Zn(OH)2 (s) +
Zn(OH)2 (s) + Zn2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq)
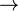 Zn(OH)2 (s)
Zn(OH)2 (s) Q2 Ammonium sulfate is heated with sodium hydroxide. (i) Write a chemical equation (include state symbols) for the reaction. (ii) Describe a test for the gas.
Answer:
(i) 2NaOH(aq) + (NH4)2SO4 (aq)
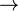 Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(L) + 2NH3(g)
Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(L) + 2NH3(g)(ii) Hold a piece of damp red litmus paper over the mouth of a test tube. It will turn damp red litmus paper blue.
Q3 An unknown green solution is heated with a piece of aluminium foil and sodium hydroxide solution. (i) The gas produced turns damp red litmus paper blue. Name the gas evolved. (ii) This is a confirmatory test for an anion. Name this anion. (iii) Give a possible cation which gives the green solution.
Answer:
(i)The gas evolved is ammonia gas.
(ii) The anion is nitrate (NO3-)
(iii) Iron(II) , Fe2+
Q4 Sulfuric acid is titrated with potassium hydroxide in the preparation of potassium sulfate salt. (i) Explain why this method is recommended for the preparation for this salt. (ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction.
Answers:
(i)Titration method is use to prepare Group(I) or ammonium salt. Potassium sulfate salt belongs to Group(I) salt. Thus, the titration method is recommended for the preparation of this salt.
(ii) H+(aq) + 2OH- (aq)
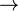 2H2O(L)
2H2O(L) Q5 Excess zinc carbonate is added to hydrochloric acid in the preparation of zinc chloride salt. (i) Write an ionic equation for the reaction. (ii) Why excess zinc carbonate is used? (iii) Briefly explain how the zinc chloride crystals can be obtained.
Answers:
(i) Zn(CO3)2 (aq) + 2HCL (aq)
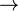 ZnCl2 (aq) + H20 (L) + CO2 (g)
ZnCl2 (aq) + H20 (L) + CO2 (g)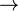
(CO3)2- (aq) + 2H+ (aq)
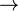 H2O (L) + CO2 (g)
H2O (L) + CO2 (g)(ii) Excess zinc carbonate will ensure that all the hydrochloric acid is completely reacted.
(iii) Zinc chloride crystals can be obtained by the excess solid + acid method. This method is used to prepare soluble but not Group(I) salt, usually Group (II), (III) or transition metals salt.
(1) Add excess zinc carbonate solid to a beaker of hydrochloric acid until there is unreacted excess solid .
(2) Filter to remove the excess unreacted solid.
(3) Evaporate the zinc chloride solution to remove the water and make a saturated salt solution.
(4) The hot saturated solution form zinc chloride salt when it is cooled.
FoReVa FrEnZ!
9/22/2011 11:01:00 pm
Friday, 8 July 2011
Shin Yoong (#05)
Clear explanantions were given. She has also drawn the atomic structures very neatly and clearly. All the information were provided and it is really good for revision. It could be seen that she has put in a lot of effort in drawing the atomic structures,finding some images from internet to further add on and the information. Maybe her answers could be present in point form to make it more clearer and easier for readers to read as it seems too wordy.
Wan Ling(#16)
Detailed and clear answers. Diagrams included were very clear and is included in our syllabus. Some additional information that are no regarding to Mr Tan's questions, like the average mass of chlorine is provided. However, on her answers to question 4, her "Definition" was misspelt.
Xue Ting(#19)
All the information given by Mr Tan was provided in her answers. All information is very clear and easy to understand especially on why is the atomic drawn this way. The atoms she draw is also very neat,nice and clear. It could be seen that she has put in a lot of effort in drawing the atomic structures. However, some of her header fonts are being overlapped. Maybe she could change to make it more clearer to readers.
FoReVa FrEnZ!
7/08/2011 08:26:00 pm
Sunday, 3 July 2011
First Question Answers
An atom has a nucleus. the nucleus is the center of the atom. An atom also has protons and neutrons at its center. Surrounding the protons and neutrons are electrons
The sub-atomic particles are protons,neutrons and electrons. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a negative charge. Since they are opposite charges they cancel each other out. Resulting in an electrical attraction between Protons and electrons. Like magnets. Neutrons are different. Neutrons are neither positive nor negative. They are neutral. ( No charge)
Example of a carbon atomic structure adapted from google:

Second Question Answers
 |
| Sodium atom (2.8.1) |
 |
| Sodium ion (2.8) |
The sodium ion is drawn this way as the sodium atom lose one electron to complete the valence shell (to make it stable), forming a positive charge of sodium ion,as the electronic ocnfiguration of sodium is (2.8.1). The maximum number of electrons in the first shell is 2. The maximum number of electrons in the second and third shell is 8.
Third Question Answers
 |
| Sulfur atom ( 2.8.6) |
 |
| Sulfide ion (2.8.8) |
Fourth Question Answers
Different atoms of the same element which have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes.
An example of isotopes would be Chlorine-35 atom and Chlorine-37 atom.
Chlorine-35 atom and chlorine-37 atom have the same number of protons (17 protons)
Chlorine-35 has 18 nuetrons.
Chlorine-37 has 20 neutrons.Since chlorine-35 atom and chlorine-37 atom have same number of protons but different number of neutrons, they are called isotopes.
Fifth Question Answers
The elements in Group(I), (II), (III) of the Periodic Table are metals. Group (III) is also known as transition metals (coloured metals).
The elements in Group (IV), (V), (VI), (VII),(VIII)/0 of the Periodic Table are non-metals.
Why is Sodium classifies as metal?
- Sodium belongs to Group (I).
- Sodium has a physical property of conducting electricity.
- Chemical property of Sodium : Sodium, whose electronic configuration (2.8.1) will lose one electron to complete the valence shell (to make it stable).
Why is Sulfur classifies as non-metal?
- Sulfur belongs to Group (VI).
- Sulfur has a physical property of not conducting electricity.
- Chemical property of sulfur: Sulfur, whose electronic configuration (2.8.6) will need to gain 2 electrons to complete the valence shell (to make it stable).
FoReVa FrEnZ!
7/03/2011 10:43:00 pm
Quetions given by Mr Tan
1. What does an atom looks like? What are the sub-atomic particles inside it.....(talk about electrons, neutrons, protons, electron shells, nucleus....)
2. Draw the atomic structure of a sodium atom and a sodium ion....explain why you draw it this way.
3. Draw the atomic structure of a sulfur atom and a sulfide ion....explain why you draw it this way.
4. Chlorine-35 atom and Chlorine-37 atom are called isotopes...Use these two examples to explain what is 'isotopes'.
5. Sodium is a metal and sulfur is a non-metal....why we classify them this way??
2. Draw the atomic structure of a sodium atom and a sodium ion....explain why you draw it this way.
3. Draw the atomic structure of a sulfur atom and a sulfide ion....explain why you draw it this way.
4. Chlorine-35 atom and Chlorine-37 atom are called isotopes...Use these two examples to explain what is 'isotopes'.
5. Sodium is a metal and sulfur is a non-metal....why we classify them this way??
FoReVa FrEnZ!
7/03/2011 10:27:00 pm










